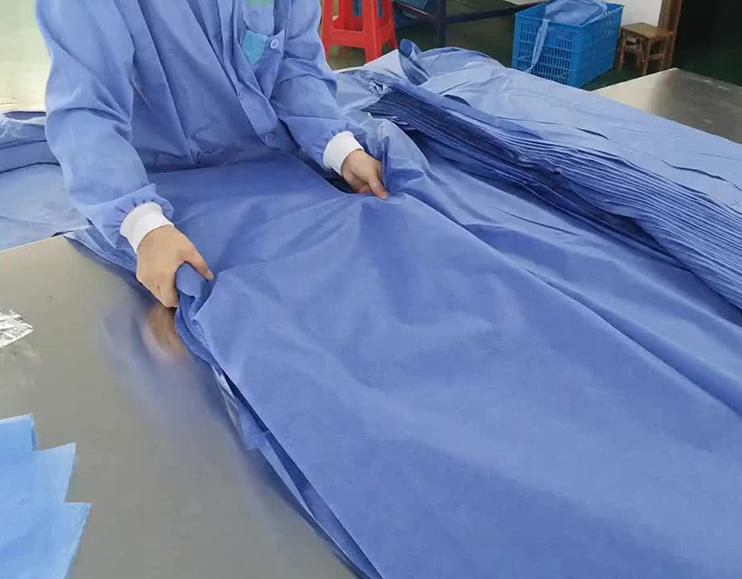
Needle-punched nonwovens are the youngest and most promising emerging field in the textile industry. The needle-punched non-woven industry in my country started relatively late, but it has developed rapidly. In the early stage of development,
needle-punched fabrics were mainly used in the clothing industry as accessories. With the rapid development of social economy and science and technology, new products and new technologies of needle-punched non-woven fabrics are emerging in an endless stream, changing with each passing day, and the scope of application is becoming wider and wider.
.jpg)
Classification of needle punched nonwovens
Non-woven fabrics break through the traditional textile principle, and have the characteristics of short process flow, fast production speed, high output, low cost, wide application, and many sources of raw materials. It is a new generation of environmentally friendly materials. Combustion-supporting, non-toxic and non-irritating, rich in color and so on.
The fibers used in the production of needle punched non-woven fabrics are mainly polypropylene (PP) and polyester (PET). In addition, there are nylon (PA), viscose, acrylic, ethylene (HDPE), and vinyl (PVC).
According to application requirements: Needle-punched non-woven fabrics are divided into two categories: disposable application type and durable type.
According to the production process is divided into:
1 Spunlace needle-punched non-woven fabric: The spunlace process is to spray high-pressure fine water flow onto one or more layers of fiber webs, so that the fibers are entangled with each other, so that the fiber webs are reinforced and have a certain strength.
2 Heat-bonded needle-punched non-woven fabrics: Heat-bonded needle-punched non-woven fabrics refer to adding fibrous or powdery hot-melt bonding reinforcement materials to the fiber web, and the fiber web is then heated, melted, cooled, and reinforced into cloth.
3 Pulp air-laid needle-punched non-woven fabric: Air-laid needle-punched non-woven fabric can also be called dust-free paper and dry-laid needle-punched non-woven fabric. It uses the air-laid technology to open the wood pulp fiberboard into a single fiber state, and then uses the air-laid method to condense the fibers on the web-forming curtain, and the fiber web is then reinforced into a cloth.
4 Wet needle punched non-woven fabric: Wet needle punched non-woven fabric is to open fiber raw materials placed in an aqueous medium into single fibers, and at the same time, mix different fiber raw materials to make fiber suspension pulp, and the suspension pulp is transported to the final product. The web mechanism, the fibers are formed into a web in the wet state and then reinforced into a cloth.
5 Spunbond needle punched non-woven fabric: Spunbond needle punched non-woven fabric is after the polymer has been extruded and stretched to form continuous filaments, the filaments are laid into a net, and the fiber net is self-bonded and thermally bonded. Bonding, chemical bonding or mechanical reinforcement methods to turn the web into a needle-punched nonwoven.
6 Melt-blown needle-punched non-woven fabric: the process of melt-blown needle-punched non-woven fabric: polymer feeding---melt extrusion---fiber formation---fiber cooling---web formation---reinforcement into cloth.
7 Needle-punched non-woven fabric: Needle-punched non-woven fabric is a kind of dry-laid non-woven fabric. Needle-punched non-woven fabric uses the puncture effect of a needle to reinforce the fluffy fiber web into cloth.
8 Stitch-bonded needle-punched non-woven fabrics: Stitch-bonded needle-punched non-woven fabrics are a kind of dry needle-punched non-woven fabrics. Plastic sheets, plastic thin metal foils, etc.) or their combinations are reinforced to make needle-punched nonwovens.
9 Hydrophilic needle-punched non-woven fabrics: mainly used in the production of medical and sanitary materials to achieve better hand feel and not scratch the skin. For example, sanitary napkins and sanitary pads use the hydrophilic function of hydrophilic needle-punched non-woven fabrics.
.jpg)